Baseline
*Content modified to protect confidentiality.
Designing a mobile application involves a user-centered approach to ensure a seamless shopping experience. Here’s my design process:
1. Define the Scope
The scope encompasses a series of questions that help define the product objectives. These questions include:
What are the product’s goals?
What does the product need to accomplish?
Who is the target audience?
What features will make the product stand out?
How do we want the product to feel?
This stage can also be called the understanding/empathy stage, as it utilizes open ended and probing questions to connect with client needs and product requirements. Conducting user research and creating user personas contribute to the scope of a product. Defining the product requirements generates ideas and ensures that the product achieves its goals.
2. Research & Discovery
Conduct market research to understand trends, competitors, and user expectations.
Gather insights through user interviews, surveys, and analytics to identify pain points in existing shoe shopping experiences.
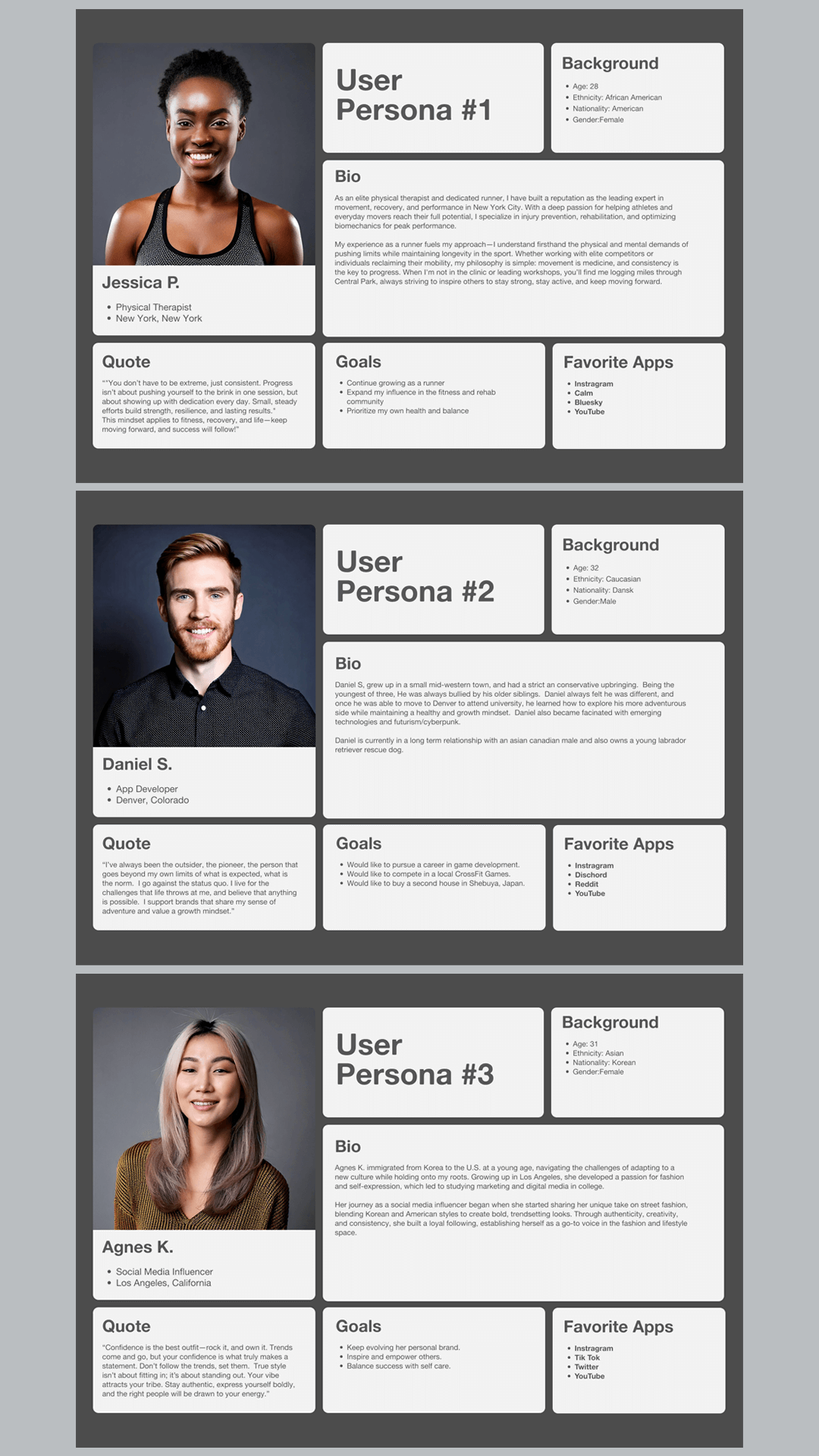
Develop User Personas
After the initial scope of a project has been established, it’s helpful to create User Personas that are based on user research, along with interviews with stakeholders and subject matter experts (SMEs). It helps identify the target audience, their behaviors, needs and pain points.
Personas ensure that design decisions are based on real user needs rather than assumptions, leading to a more user-friendly experience. They help designers empathize with users by giving them a clear picture of their goals, frustrations, and motivations.
With personas, teams can make informed decisions about design elements, features, and content that best serve the users.
Personas provide a shared reference point for designers, developers, marketers, and stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned on who the users are.
By understanding user behavior early on, teams can avoid costly design changes later and focus on creating intuitive and effective experiences.
Personas help in designing experiences that cater to different types of users, improving engagement and satisfaction.
They serve as a benchmark for usability testing, allowing teams to validate if their designs meet the needs of the intended users.
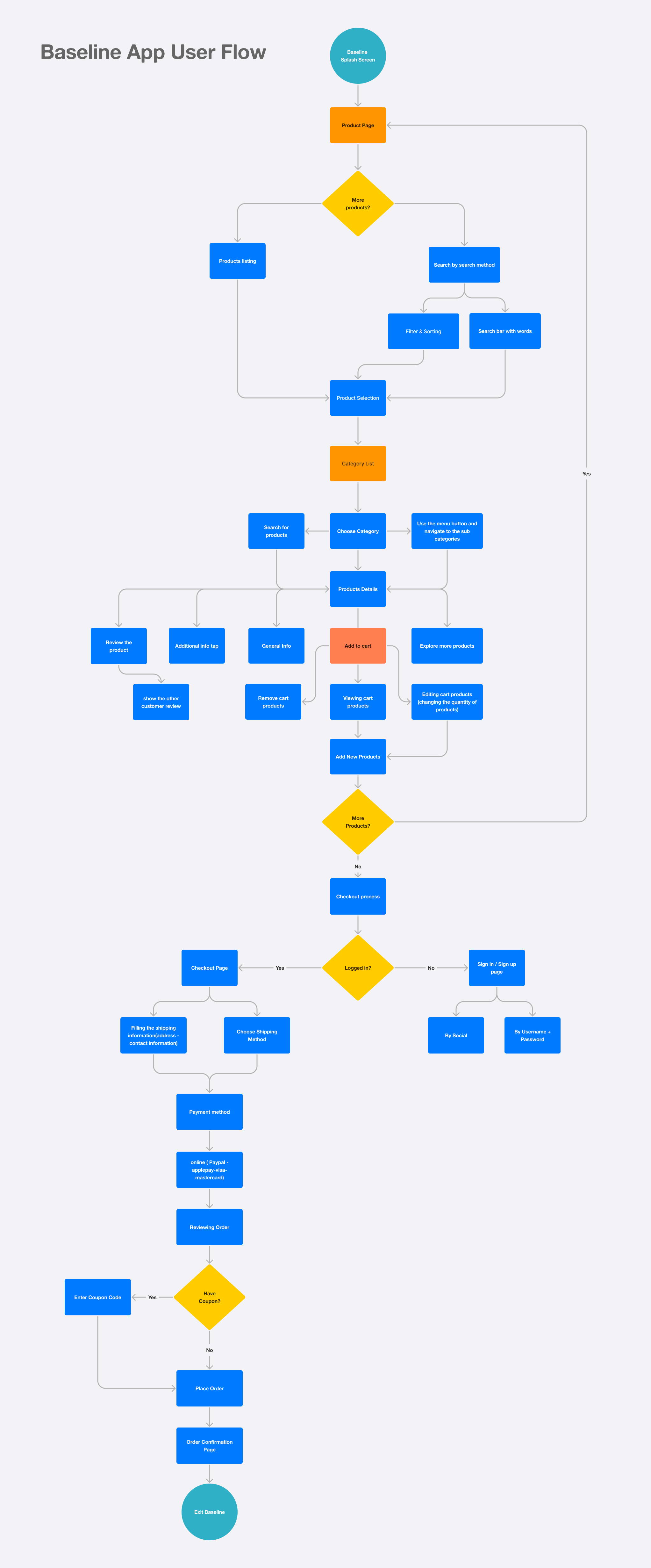
3. Define Requirements & User Flows
Outline core features: product browsing, filtering, personalized recommendations, secure checkout, order tracking.
Map out user journeys from product discovery to purchase to ensure an intuitive flow.
Prioritize accessibility and inclusivity, ensuring the app is usable for all customers.
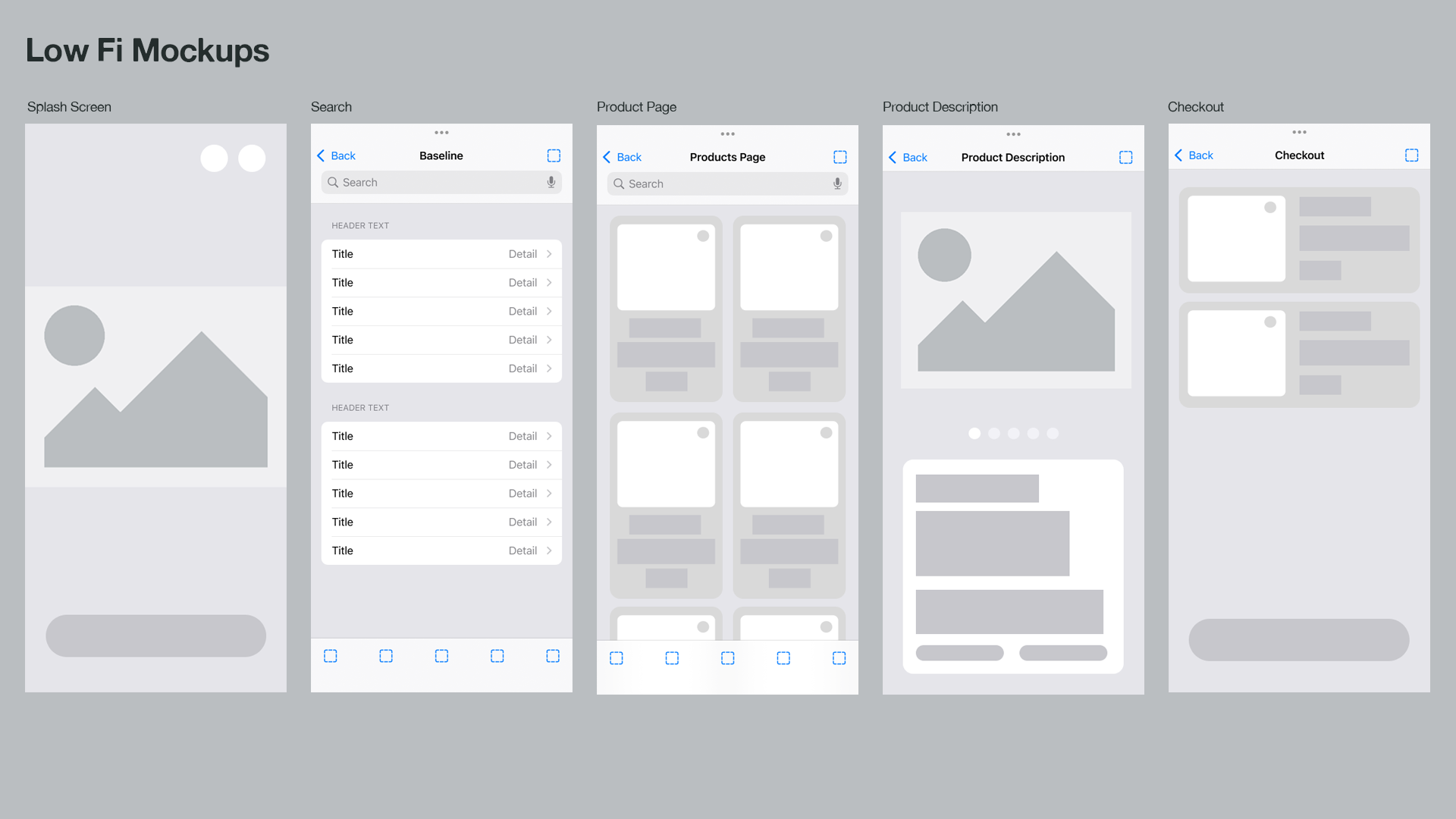
4. Wireframing & Prototyping
Create low-fidelity wireframes to outline the structure and layout.
Develop interactive prototypes to test usability before moving into visual design.
Conduct usability testing with real users and refine based on feedback.
Wireframe
Wireframes serve as a visual representation of a product, forming the foundation of the user flow. They provide a high-level overview of a product, excluding intricate details. Subsequently, wireframes can be transformed into low and high fidelity mockups of the product.
Prototype
A prototype is an interactive sample of a product that showcases its features and functionalities. Clients or stakeholders can make informed decisions about the design, layout, and functionality of the prototype before approving the product for implementation.
Creating the User Interface (UI) of a product is crucial for defining its visual appearance and shaping its product identity and ensure usability before visual design and high fidelity mockups can be developed.
5. UI/UX Design
Implement a modern, mobile-friendly design with high-quality visuals and an engaging user interface.
Focus on microinteractions and animations to enhance the user experience.
Ensure a consistent design system with intuitive navigation and clear calls to action.
6. Development & Implementation
Collaborate with developers to build a scalable and responsive mobile application.
Optimize for performance and speed, ensuring fast loading times and smooth interactions.
Implement secure payment gateways and account authentication for user safety.
Development
Once the design prototype is approved, it is handed over to the developers to build the product. At this stage, the designer assumes the role of the lead consultant, ensuring the product’s integrity and addressing any potential obstacles that may arise with stakeholders.
7. Testing & Iteration
Conduct extensive testing (functional, usability, and A/B testing) to identify and fix issues.
Optimize for different devices and operating systems to ensure compatibility.
Gather user feedback and iterate on features based on real usage data.
Testing
Once the product completes development, it is important to conduct User Acceptance Testing and to ensure that the product meets client product requirements. Collecting feedback from designers and developers will help refine any final adjustments to a product and project completion.
8. Launch & Continuous Improvement
Deploy a beta version for early adopters to test.
Monitor analytics and user behavior to measure success.
Continuously update the app based on user feedback, trends, and technology advancements.